What is the Most Sustainable Gemstone?
With growing awareness around sustainability and ethical sourcing, many consumers are looking for gemstones and jewelry that are environmentally friendly and responsibly sourced. But with so many different types of gemstones on the market, it can be tricky to identify which are the most sustainable options. In this article, we'll take a look at some of the most sustainable gemstone and mining practices, and explore which gemstones have the smallest eco-footprint.
An Overview of Sustainable Gemstones
So what exactly makes a gemstone sustainable? Sustainably-sourced gemstones are those that are mined and processed with minimal environmental impact. This includes utilizing mining practices that do not damage habitats or contribute to deforestation. It also means avoiding dangerous working conditions and underpaying miners in developing countries.
Some key factors that determine how sustainable a gemstone is include:
- Mining methods: Does the mining process cause minimal disruption to the surrounding habitat? Some methods like strip mining are highly destructive. More sustainable practices include tunnel/underground mining.
- Reclamation: Are habitats and landscapes restored after mining operations cease? Responsible mining includes reclamation plans.
- Labor practices: Does the mining company avoid child/forced labor and dangerous working conditions? Ethical labor practices are a key component.
- Environmental impact: How much energy, water, and chemical use is required to mine, cut, and polish the gemstone? Lower environmental impact equals more sustainability.
- Abundance: Is the gemstone relatively abundant or scarce? Abundant gemstones are often more sustainable.
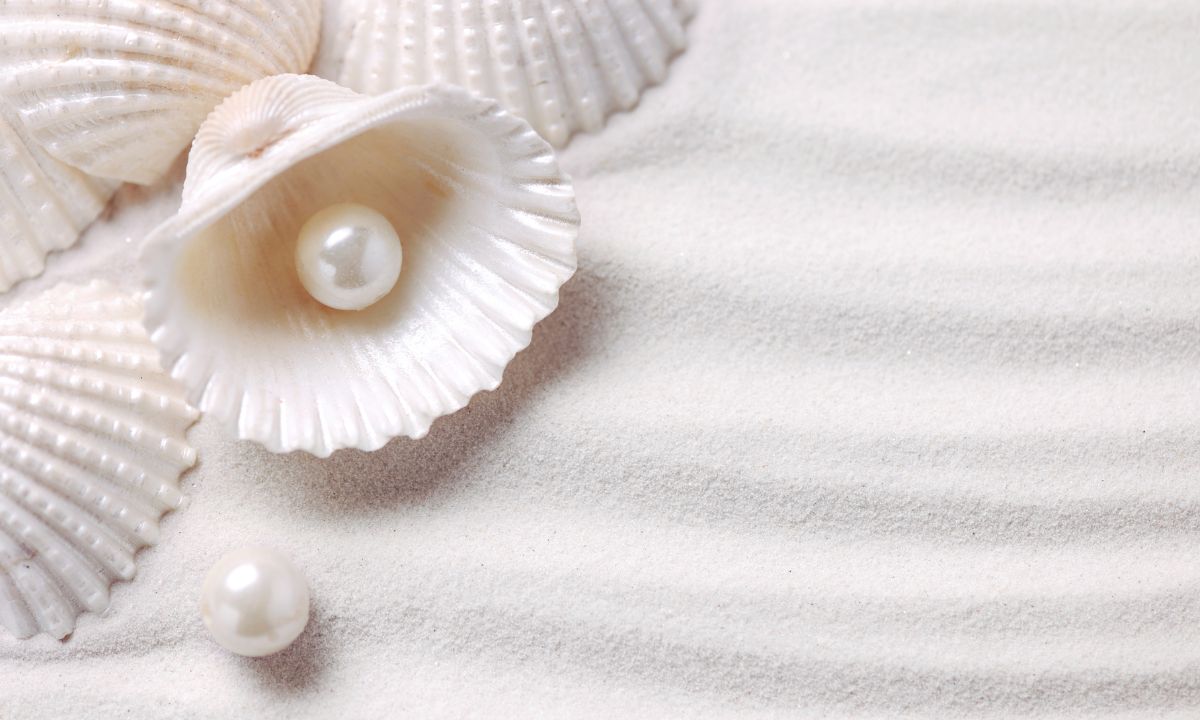
Why Pearl Farming is the Most Sustainable
When evaluating all these criteria, one type of gemstone stands out as the most sustainable - pearls. Natural pearls form when an irritant like a parasite or sand gets lodged in an oyster or mussel's shell. As a defense mechanism, the mollusk secretes a fluid called nacre to coat the irritant. Over time, layers of nacre build up to form a lustrous pearl.
These days, the vast majority of pearls on the market are cultivated rather than natural. Pearl farming is an aquaculture practice in which mollusks like oysters and mussels are raised specifically for pearl production. Through a surgical process, a nucleus bead is inserted into the mollusk along with a piece of mantle tissue from a donor mollusk. The implanted mollusk is then placed into a controlled pearl farm environment to stimulate nacre secretion and pearl growth.

Why Pearl Farming is Sustainable
There are several reasons why pearls stand out as the most sustainably-sourced gemstone:
- No mining required: Pearls are farmed in controlled aquatic environments, so there is no need for mining or disruption of natural habitats. No deforestation, strip mining, or habitat damage is associated with pearl cultivation.
- Abundant: Pearl farms can generate a relatively abundant supply of pearls without depleting limited natural resources. The availability of cultured pearls reduces harvesting pressure on wild mollusk populations.
- Environmentally friendly: Pearl farming has a low carbon footprint and relatively minimal environmental impact compared to gemstone mining. No excavation, energy-intensive cutting/polishing, or chemical processing is required.
- Economically beneficial: Pearl farming provides livelihoods and income for coastal communities globally. Especially in developing regions, pearl farms create jobs and economic opportunities in an eco-friendly way.
- Prevents overfishing: Pearl farms give mollusks economic value, which incentivizes protection of wild stocks. Farming pearls reduces the need to overharvest wild oysters.
- Habitat creation: Oyster farms and pearl farm environments serve as artificial reefs which attract marine life. They ultimately create habitat and promote biodiversity.
So by avoiding destructive mining practices and offering environmental benefits, pearl farming sets the standard for sustainability in gemstone production. Let's take a more detailed look at what makes pearls such an eco-friendly choice.
The Environmental Benefits of Pearl Farming
Pearl farming earns top marks when it comes to having a low ecological impact. Here are some of the main ways that pearl cultivation protects the planet:
No Mining or Deforestation
Unlike mining precious metals or gemstones like rubies and sapphires, producing pearls does not require digging up the earth. There is no need for energy-intensive mining machinery or blasting through mountains. Without mining, there is no infrastructure development, deforestation, or large-scale disruption of landscapes. Lands remain untouched, and natural habitats are preserved.
Clean Aquaculture Practice
Reputable pearl farms use responsible aquaculture practices with proper waste management. Waste from the oysters is discharged into the ocean where it becomes integrated into the ecosystem. Farms monitor water quality and aim to avoid pollution or impacts on surrounding fisheries or coral reefs. With clean aquaculture practices, pearl farming does not create pollution or carbon emissions on par with mining operations.
Low Energy Requirements
Aside from the energy needed to run boats and on-shore facilities, pearl farming has low energy demands. No excavation equipment or processing facilities are necessary. The oysters feed by filter-feeding from the natural environment, so providing food does not require major energy inputs. With minimal power needs, pearl cultivation emits few greenhouse gases and has a small carbon footprint.
No Enhancements or Treatments
After harvest, pearls do not require any treatments or enhancements like heating or irradiation to improve their luster and color. The lack of post-harvest processing makes pearls a more environmentally sustainable choice compared to treated gemstones. Pearls go directly from the farm to market with no energy-intensive cut, polishing or enhancement steps.
Biodegradable Nuclei
To induce nacre secretion, pearl farms insert a nucleus bead along with a slice of mantle tissue into each oyster. These starter nuclei were traditionally made from shell, but the majority today use non-toxic, biodegradable resin beads. This makes pearl farming even more eco-friendly, as the nuclei will harmlessly biodegrade if ever released into the environment.

Thanks to practices like these, pearl production has a light environmental footprint. Pearl farms protect ecosystems while generating abundant renewable gemstone resources.
The Most Sustainable Pearl Types
Not all pearls are created equal when it comes to sustainability. Several factors can influence an individual pearl's eco-rating, like:
- Location - Pearls farmed in pristine environments with strict regulations generally rank higher. Australian and U.S. pearl farms adhere to top environmental standards.
- Farming methods - Some have more controls in place to prevent ecological impacts. For example, longline farms have minimal seabed contact.
- Nucleus materials - Fully biodegradable beads are ideal. Some lower-grade nuclei still contain shell fragments.
- Color enhancement - Non-enhanced pearls are considered most natural and sustainable.
Here are some of the most sustainable pearl varieties that eco-conscious buyers should know about:
Akoya Cultured Pearls
Grown primarily in Japan and China, Akoya pearls have a golden complexion and classic elegance. Their small size also means fewer resources go into each pearl. With a long history of pearl farming, Japan closely monitors water quality and enforces environmental regulations. This makes Japanese Akoya pearls a more sustainable pick.
Freshwater Cultured Pearls
China dominates freshwater pearl production, but U.S. farms also cultivate these popular pearls sustainably. The freshwater mussels are farmed in ponds, lakes or reservoirs for maximum environmental control. Plus, freshwater pearls use only a tiny piece of mantle tissue from one donor mussel to seed hundreds of recipients.
Tahitian Black Pearls
French Polynesia exercises strict oversight of its iconic black pearl farms. Regulations help prevent environmental impacts and maintain the pristine ocean waters that give Tahitian pearls their dark, mysterious beauty. These exotic cultured pearls have high sustainability marks.
U.S. Farmed Pearls
American pearl farms lead the way in sustainable practices. With federal and state environmental protections in place, U.S. pearls from California, Tennessee, and Hawaii meet the country's highest sustainability benchmarks while funding conservation initiatives.
Responsibly Farmed South Sea Pearls
White and golden South Sea pearls hail from Australia, Indonesia and the Philippines. Australian production has the most oversight to produce South Sea pearls sustainably. Their pristine warm waters give these larger pearls their silver-blue sheen.
Pearl aficionados looking to make an eco-friendly choice should look for these sustainably farmed pearl varieties.
Are There Other Sustainable Gemstone Options?
Although pearl farming is the frontrunner when it comes to sustainability, other responsibly-sourced gemstones also make ethical alternatives. Here are some other eco-friendly options to consider:
Sapphires
While large-scale sapphire mining can have environmental impacts, small-scale, artisanal mining in places like Sri Lanka uses less invasive methods. Looking for sapphires from small ethical mines is a more sustainable choice.
Rubies
Like sapphires, aim for rubies from small-scale ethical mining operations. Rubies found along Kenya’s Tsavo river are alluvial, meaning they can be collected from stream sediment with minimal digging or habitat destruction.
Colored Gemstones from Afghanistan
Afghanistan's long tradition of colored gemstone mining provides vital economic opportunities in this developing nation. Afghan emeralds, rubies, and lapis lazuli help support local communities when purchased ethically.
Canadian Diamonds
Selecting natural diamonds from Canada’s sustainable mining operations is an eco-friendly alternative to mining in developing nations with fewer regulations. The country’s diamond industry demonstrates how mining can be done responsibly.
Lab-Grown Gemstones
Opting for lab-created versions of precious gems like rubies and emeralds eliminates the need for mining entirely. While the manufacturing process does use energy, it has less ecological impact overall.
Fair Trade Gold
Choosing fair trade gold for settings can complement responsibly-sourced gemstones. Fair trade gold comes from artisanal, small-scale mines that adhere to strict environmental and labor standards.
So while pearl farming remains the most sustainable option, discerning consumers can find alternative gemstones and metals with ethical sourcing in mind as well.

The Future of Sustainable Pearls
Thanks to consumer interest, the future looks bright for environmentally responsible pearls. With global demand, pearl farmers are investing in sustainability practices to preserve the coastal ecosystems that allow their businesses to thrive.
Some developments to look for include:
- New sustainable pearl farming regions emerging
- Continued progress on biodegradable nucleus development
- Genetic selection to breed more resilient oyster stocks
- Advances in off-shore and hybrid pearl farming methods
- Innovations in pearl farming equipment and technology
- Expansion of sustainability certifications for pearl farms
Today’s pearl farmers are stewards of their marine environments and champions of sustainable gemstone production. With their efforts and consumer support, the pearl industry is poised to continue leading the way in eco-friendly jewelry practices.
How to Buy Sustainable Gemstones Responsibly
Once you’ve chosen a more eco-friendly gem, it’s equally important to ensure it’s sourced responsibly. Here are a few best practices to buy gemstones:
- Review any associated sustainability reports from the mining company or location. Many ethical mines publish detailed accounts of their practices.
- Ask jewelers lots of questions about where and how their stones are sourced and mined. Reputable sellers should know and be proud to share their origins.
- Look for respected sustainability certifications from groups like the Responsible Jewellery Council, Fairmined metals, and SCS Global Services.
- Seek out independent sustainability audits that verifies responsible sourcing.
Conclusion
For shoppers who care about minimizing environmental damage, pearls are clearly the stand-out choice. As a renewable gemstone farmed in controlled settings, pearls have the lowest eco-impact of any jewelry available today. By choosing responsibly-sourced pearls, consumers can feel good knowing their purchase isn’t harming the planet.
Pearls top the list for their abundance, natural beauty, and environmental sustainability. Farmed pearls put other gemstones mined from the earth to shame when it comes sustainability. Environmentally-conscious jewelers and buyers should make cultured pearls their go-to gem.
So when shopping for eco-friendly jewelry, look for sustainably-farmed pearls first. Their brilliance reflects the natural wonder of oysters and mollusks while safeguarding those marine treasures for the future. Thanks to pearl farmers’ stewardship, pearls will continue shining as the world’s most lustrous and sustainable gemstone.